
Wood from trees grown for industrial purposes, such as pine, eucalyptus and teak, is gaining ground as an innovative and sustainable solution for the construction industry. These trees are not only a source of renewable raw materials, but also help capture and store carbon from the atmosphere, mitigating the effects of climate change. Opting for wood contributes to cleaner and more sustainable construction.
Construction is one of the human activities that consumes the most natural resources. In Brazil, for example, construction generates around 25% of industrial waste and 60% of solid waste in cities. Globally, the sector accounts for 47% of greenhouse gas emissions, according to WWF Nature, and buildings consume 40% of the world’s energy, according to UNEP.
Adopting cleaner practices is essential to meet these challenges, focusing on renewable raw materials. One of the best options is the use of construction systems involving timber from planted trees, especially high-tech options.
Building with wood from planted trees offers several advantages that impact both the environment and the consumer. The main advantage is speed of construction, since the use of prefabricated components and simpler foundations means construction time is up to 50% shorter than when other traditional materials are used. Using wood also generates less waste (a reduction of 20% to 30%), which contributes to cleaner and more efficient construction projects.
The lighter weight of wood is another highlight: wooden buildings can weigh up to 1/5 of conventional buildings. This means fewer truck trips to transport the materials, reducing CO₂ emissions during the process. From an environmental point of view, wood also stands out for its ability to capture carbon during tree growth, store this carbon in the product, and replace fossil-based inputs and raw materials, which directly helps to mitigate climate change.
Finally, there are also important social benefits such as job creation and qualification of the workforce involved in the wood construction process, promoting sustainable practices and valuing specialized labor.
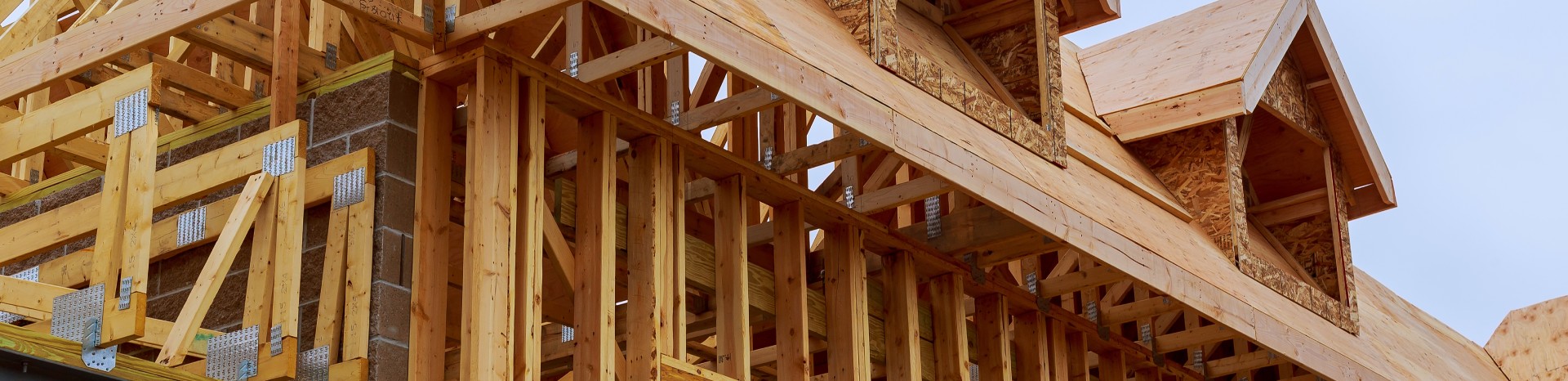
Wood can be used in home construction in finishes, concrete forms, and structure. The main types of wood and their applications are:
Mechanically processed wood

This wood is usually chemically treated to be more durable. It can be used for finishing, concrete forms and structural purposes. Applications: heavy external (bridges, walkways, shoring, etc.); light external and internal structural (scaffolding, shoring and concrete forms); light in frames (doors, shutters and moldings); heavy internal (pillars, beams and rafters); light internal (ceilings, paneling, decorative panels and trim).
Rough wood that is cut and dried and can be finished using pneumatic planers. It can be used for finishing, concrete forms and structural purposes. Applications: heavy external (bridges, walkways, shoring, etc.); light external and internal structure (scaffolding, shoring and concrete forms); light use in framing (doors, shutters and moldings); heavy internal uses (pillars, beams and rafters); light internal uses (ceilings, paneling, decorative panels and trim).
Made up of thin sheets glued in opposite directions for greater strength. It can be used as temporary sheathing for building sites, slabs, beams etc.
Structural, made up of layers of wood glued together with moisture-resistant adhesives. It is suitable for beams, pillars, walkways, roofs, stairs, panels and various coatings.
Made from wood fibers bonded by heat and pressure, without the use of synthetic resins. It is indicated for production of home and office furniture, cabinet and drawer bottoms, packaging goods from a variety of industries for storage on pallets, dividing panels, and in applications in the automotive, packaging, toy, sound/image, fruit/vegetable and construction sectors.
Strips of wood glued together in perpendicular layers, used for siding, scaffolding and concrete forms.
Reconstituted wood
Medium-density particleboard, used in furniture, shelves and partitions.
Medium-density fiberboard, ideal for lathing and machining.
High-density fiber or particleboard, respectively, used in laminate flooring and partitions.
Made of wood particles and highly resistant to abrasion, guaranteeing durability.
Innovative technologies
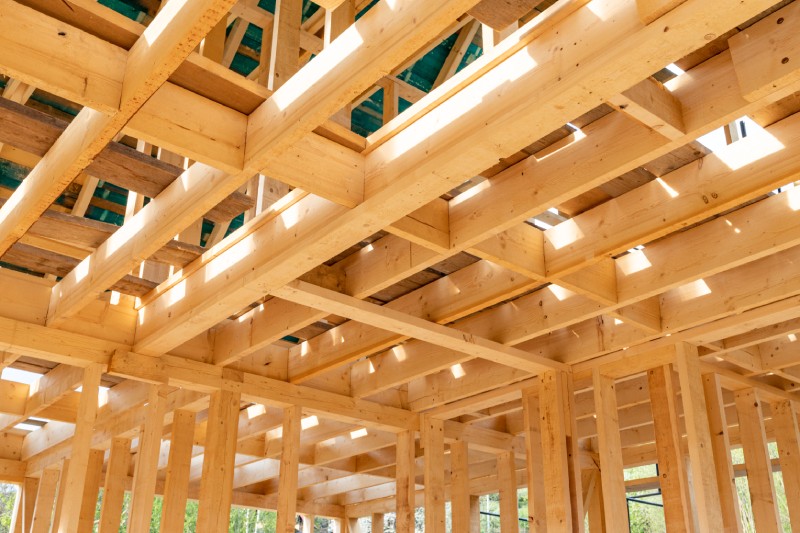

Panels with several layers of solid wood veneer glued in opposing directions. This technology makes it possible to construct skyscrapers out of wood.
Structural alternatives used in large construction projects.
A construction system that uses wood profiles and panels for closing.
These industrialized wood options represent the future of construction, combining technology, sustainability and efficiency for a more conscious and innovative sector.